Standardize processes across cells, lines, or entire sites without the overhead of traditional MES.
Modular MES: The Modern Approach to Scalable Factory Operations

Identify Error-Prone Areas
Pinpointing the areas most susceptible to errors is the foundation for a successful error-proofing strategy.
- Conduct a Production Audit
Begin by analyzing production data, quality control reports, and incident logs to identify recurring issues. Are there specific steps or stations where defects frequently occur? Focus on both human and machine-related errors. - Involve Frontline Workers
Your factory workers are often the first to detect potential problems. Encourage them to share insights about where and why errors happen. Their feedback can reveal valuable information that might not be captured in data alone. - Use Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Addressing the surface issue isn’t enough. Use tools like 5 Whys or Fishbone diagrams to trace errors back to their origin. This ensures that you’re solving the root causes of mistakes, not just treating the symptoms. - Identify High-Risk Processes
Prioritize error-proofing efforts in processes or stations where errors are both frequent and costly. In industries like aerospace or medical device manufacturing, even small mistakes can have severe consequences, making these areas critical candidates for error-proofing.
Choose the Right Tools for Your Needs
Once you’ve identified the most error-prone areas in your process, it’s time to select the right error-proofing tools and technologies that can help address those specific issues. It’s important to remember that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, as different processes and error types require different tools.
- Evaluate Existing Solutions
Review the tools already in place. Are manual checks being used where automation could improve accuracy? Are physical poka-yoke devices still effective, or are they outdated? - Consider the Nature of Errors
- For human errors: If your issues stem from human mistakes (e.g., incorrect assembly or missing parts), consider digital solutions like real-time visual prompts, guided instructions, or automated feedback systems that alert workers when errors occur.
- For machine-related errors: If machines are responsible for frequent errors, automated quality checks and real-time equipment monitoring can prevent downtime and ensure consistency.
- Decide on Digital or Physical Error-Proofing
Traditional error-proofing methods rely on mechanical devices like jigs or limit switches. While effective, these tools are reactive. Modern error-proofing systems provide digital solutions that are more flexible and scalable. For instance, PICO’s real-time monitoring and error-detection software helps you respond to shop floor issues faster and make quicker decisions, enabling manufacturers to adapt effectively to changing conditions.
Pilot the Process on a Small Scale
Before rolling out your error-proofing solution across the entire production line, it’s best to pilot it in a controlled environment. A pilot allows you to test the effectiveness of your tools, make necessary adjustments, and build confidence before full-scale implementation.
- Select a Pilot Area
Choose a station, line, or product to test your error-proofing tools. Ideally, this should be an area that experiences frequent or costly errors, based on the findings from Step 1. - Set Clear Objectives
Establish measurable goals for the pilot. For example, you might aim to reduce defects by a specific percentage or minimize rework time. Defining these metrics upfront will help you evaluate the success of the pilot and guide future rollouts. - Monitor Performance Closely
During the pilot, track error rates, production efficiency, and worker feedback to gauge how well the tools are functioning. Take note of any issues or challenges that arise, as these can inform improvements in broader implementation. - Be Open to Iteration
Piloting is an iterative process. Expect to discover areas for improvement, and be ready to adjust your system based on feedback. This phase allows you to refine the approach, ensuring maximum effectiveness during full-scale rollout.
Train and Support Your Team
Technology alone can’t drive error-proofing, your team’s understanding and buy-in are equally important. Proper training and ongoing support are crucial for success.
- Design Hands-On Training
Provide hands-on training to your workers. For instance, if you’re implementing PICO’s real-time error detection system, ensure employees practice using digital prompts and alerts in their day-to-day tasks. - Provide Continuous Learning Resources
Equip workers with digital resources like video tutorials, interactive guides, and quick-reference materials to reinforce training. Modern error-proofing systems like PICO offer real-time prompts and instructions, making it easier for workers to adapt. - Encourage Ownership and Accountability
Employees are more likely to engage with error-proofing initiatives when they feel a sense of ownership. Encourage them to identify potential errors in their processes and suggest improvements. Establishing a feedback loop where workers can share their experiences ensures continuous improvement. - Support Cross-Functional Training
Cross-functional training builds a more resilient workforce. When employees understand the full production process, they’re better equipped to spot errors before they occur.
Monitor and Optimize the System Continuously
Error-proofing isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it solution. Continuous monitoring and optimization are key to long-term success.
- Use Data to Drive Improvements
Modern error-proofing systems like PICO’s provide real-time data on production efficiency and error trends. Use these insights to make data-driven decisions about where further improvements are needed. - Regularly Audit Error Rates
Conduct regular audits to track error rates, defect occurrences, and rework data. Are certain errors still slipping through? Are there areas where performance has improved dramatically? Use this data to tweak your systems for optimal performance. - Adapt to Changing Conditions
Manufacturing environments are constantly evolving. Whether it’s new equipment, changing product lines, or shifts in workforce dynamics, your error-proofing tools should be flexible enough to adapt.. - Solicit Continuous Feedback
Encourage workers and managers to offer ongoing feedback about how error-proofing tools are functioning. Are there frustrations or gaps that need to be addressed? Continuous feedback is essential to evolving your system as conditions change. - Benchmark Your Progress
Compare performance data before and after error-proofing implementation to measure improvement. Benchmarking your progress not only demonstrates the ROI of your investment but also ensures ongoing refinement of your systems.
In assembly manufacturing, agility, flexibility, and scalability are more than buzzwords–they’re necessities. As manufacturers strive to modernize their operations, many are confronting a major challenge: outdated, monolithic Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). These legacy systems, once considered cutting-edge, are now becoming a bottleneck to innovation. In this guide, we’ll explore the challenges with legacy MES and introduce its solution: Modular MES–a modern, nimble system design that’s transforming how assembly manufacturers operate and scale.
Why Don't Legacy MES Systems Work Anymore?
Legacy MES platforms were designed during an era when large, centralized systems ruled the enterprise software world. These systems aimed to provide a comprehensive solution for managing manufacturing operations, offering everything from production scheduling and quality management to traceability and manufacturing KPI tracking–all under one roof.
But these “all-in-one” systems often come with significant drawbacks, including high costs and complex licensing structures, significant investments in IT infrastructure, resource-intensive maintenance, long deployment times, and feature bloat–meaning you’re stuck paying for more than you realistically need or use.
These systems are also associated with low return-on-investment, where the complexity and rigidity often lead to poor adoption on the shop floor and underwhelming results not just in the factory, but for the business as a whole. These pain points have driven manufacturers to seek more agile, cost-effective alternatives.
Read more about how legacy software is killing your factory's productivity.
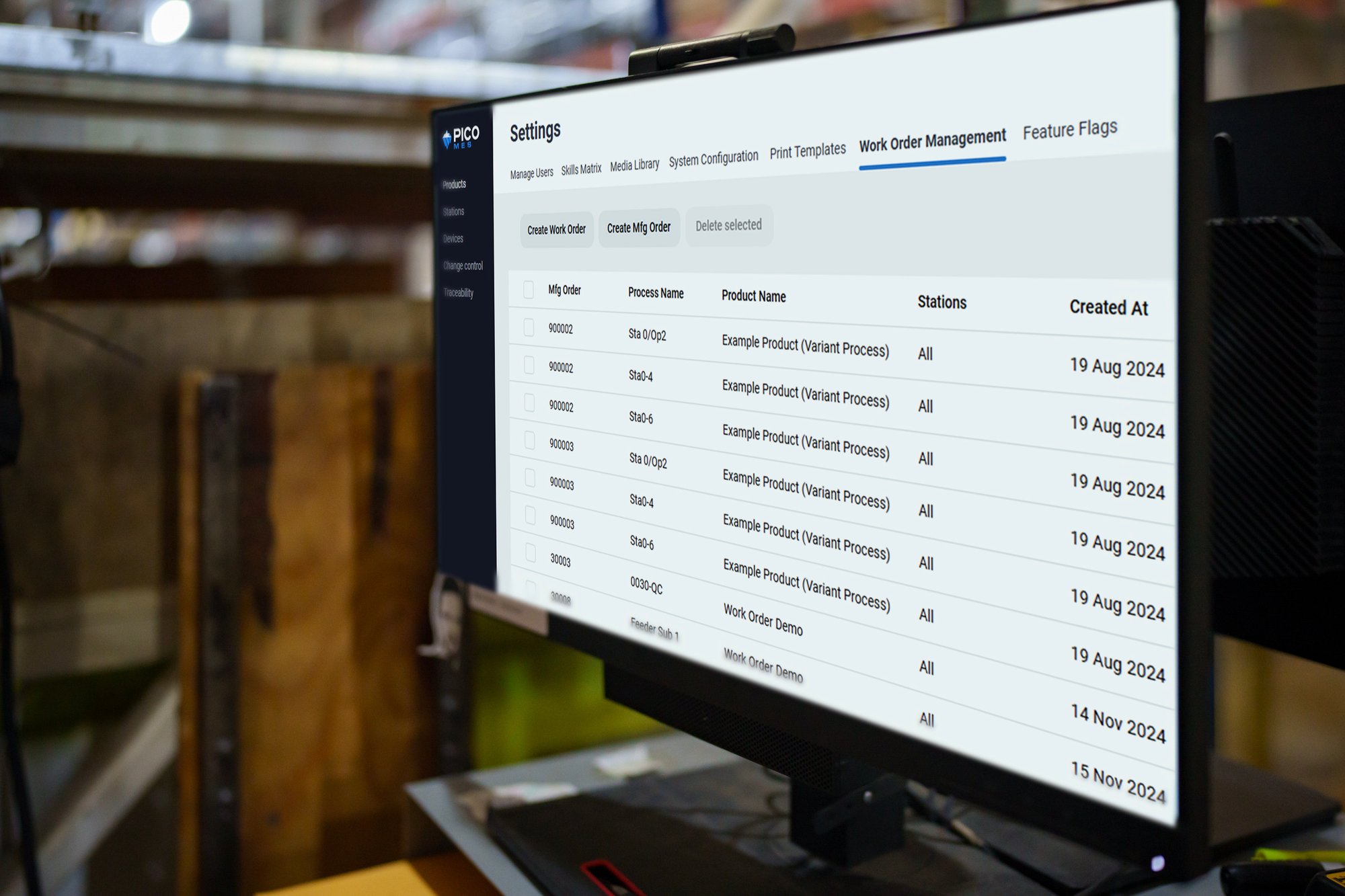
What is Modular MES?
A modular MES is a flexible, feature-based platform that allows manufacturers to deploy only the capabilities they need, such as digital work instructions, traceability, or smart tool integration, without having to implement a full suite all at once. This reduces deployment time, cost, and complexity compared to traditional monolithic MES platforms.

Here's what sets modular MES apart:
- Buy only what you need: Pay for core functionality first (e.g. work instructions or tool integrations), then expand later as your operation and needs grow.
- Faster deployment: With fewer moving parts, modular MES systems can be deployed in weeks, not months.
- Frontline-friendly: Simpler, more intuitive interfaces and automated data collection make adoption easier for operators, improving user experience and process efficiency.
- Scalable architecture: Start small in a single cell or line, then scale up to other lines or sites without ripping and replacing your system.
In short, modular MES gives manufacturers the flexibility to adapt quickly while reducing risk and cost.
Looking for advice on how to implement a new error-proofing and shop floor management system strategically? Get a digital transformation roadmap for first-time Ops leaders.
Why Now? The Modern Shift Towards Modular MES
Today, manufacturers are navigating an entirely different landscape: high-mix low-volume assembly, rising product complexity, disconnected software ecosystems, and a skilled labor shortage that’s reshaping the factory floor.
Traditional MES deployment models weren’t designed for this level of speed, customization, or scale. That’s why more manufacturers are transitioning to modular MES platforms; modern, flexible systems built to support rapid deployment, seamless ERP and MES integration, and incremental growth.
What's Changed on the Shop Floor?
1. High-Mix, Fast-Changing Production Environments
Manufacturers today must support a growing number of SKUs, options, and build variants. In traditional MES systems, even small engineering changes require heavy configuration or IT support. A modular MES enables faster updates, version control, and MES modules that can be swapped or added as needed, ideal for high-mix low-volume production.
2. Labor Turnover and Onboarding Pressure
With high operator turnover and shrinking pipelines for skilled workers, there’s a growing need for intuitive, paperless manufacturing tools that guide the frontline with less supervision. Digital transformation in manufacturing isn’t just about data; it’s about delivering real-time, easy-to-follow information where it matters most.
3. Disconnected Tech Stacks and Data Silos
Modern factories rely on multiple systems: ERP, QMS, PLM, and often homegrown spreadsheets. Monolithic MES platforms struggle to connect the dots. Modular MES systems are designed for ERP and MES integration and other cross-platform connections, helping manufacturers reduce data duplication and improve transparency across departments.
4. Need for Speed and Agility
Whether you're adding a new cell, fixing a process bottleneck, or rolling out error-proofing solutions, manufacturers no longer have 6–12 months to deploy changes. An MES with plug-and-play modules allows you to launch quickly, scale incrementally, and adapt on the fly, supporting real-world agility without overwhelming your team.
But Wait - Isn't There Something Called "Composable MES" Too?
As more software vendors rebrand their offerings for modern factories, terms like modular MES and composable MES are often used interchangeably. But while they’re related, they aren’t the same, and understanding the difference can help you choose the right solution for your operation.
Composable MES takes modularity a step further, into the architecture and development philosophy behind the system. First coined by analysts like Gartner and promoted by companies like Tulip, a composable MES is typically:
- Cloud-native and built on microservices
- Driven by open APIs and common data models
- Designed to be customized or extended using no-code/low-code development environments
- Built with governance tools to support "citizen developers" on the factory floor
Composable MES platforms are often developer-oriented and require a certain level of internal technical capability. The promise is that manufacturing engineers or even frontline staff can “compose” their own solutions using building blocks, creating apps, dashboards, and workflows tailored to their unique needs.
What are the Differences Between Modular vs. Monolithic MES?
Capability |
Modular MES |
Legacy MES |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility |
Designed to solve specific problems. Only pay for and deploy the features you need, when you need them. |
Designed to be “one size fits all”. Custom module creation requires dedicated solution architects. |
IoT Integrations |
Unlimited brand-agnostic tool, device, and equipment integrations. All free, all no-code. |
IoT connectivity is expensive and requires hardware integration specialists. May be limited to a specific brand of tools. |
Scalability |
Start at a single station and expand to multiple stations or full production lines when you’re ready. |
Difficult to accommodate different stations running different tasks, making expansion a headache. |
Cost Effectiveness |
Digital work instructions are free, forever. |
Expensive, complex licensing structures and additional fees for add-on features and services. |
Deployment |
Lightweight, cloud-based or optional hybrid/on-premise deployments. Set up and start building in hours, not weeks. |
Takes months to implement, and even longer to learn how to use. |
Support & Maintenance |
Dedicated Customer Success team members are available via email, Slack, or MS Teams chat for same-day responses. |
Tech support available at additional cost and with slow response times. |
User Training |
Designed for all operators of all skill levels. |
Specialized training required; skills gap will be noticeable. |
Who is Modular MES For?
Modular MES is designed to meet the needs of cross-functional teams in manufacturing.
Manufacturing Engineers
Accelerate iteration, reduce rework, and update build processes without software bottlenecks.
Quality Managers
with less manual effort.
IT Managers
Key Features of Modular MES
Modern modular MES platforms are designed to plug into the unique workflows of assembly manufacturers.
Digital Work Instructions
Replace paper-based worker guidance with dynamic, visual instructions that update in real-time and ensure process adherence.
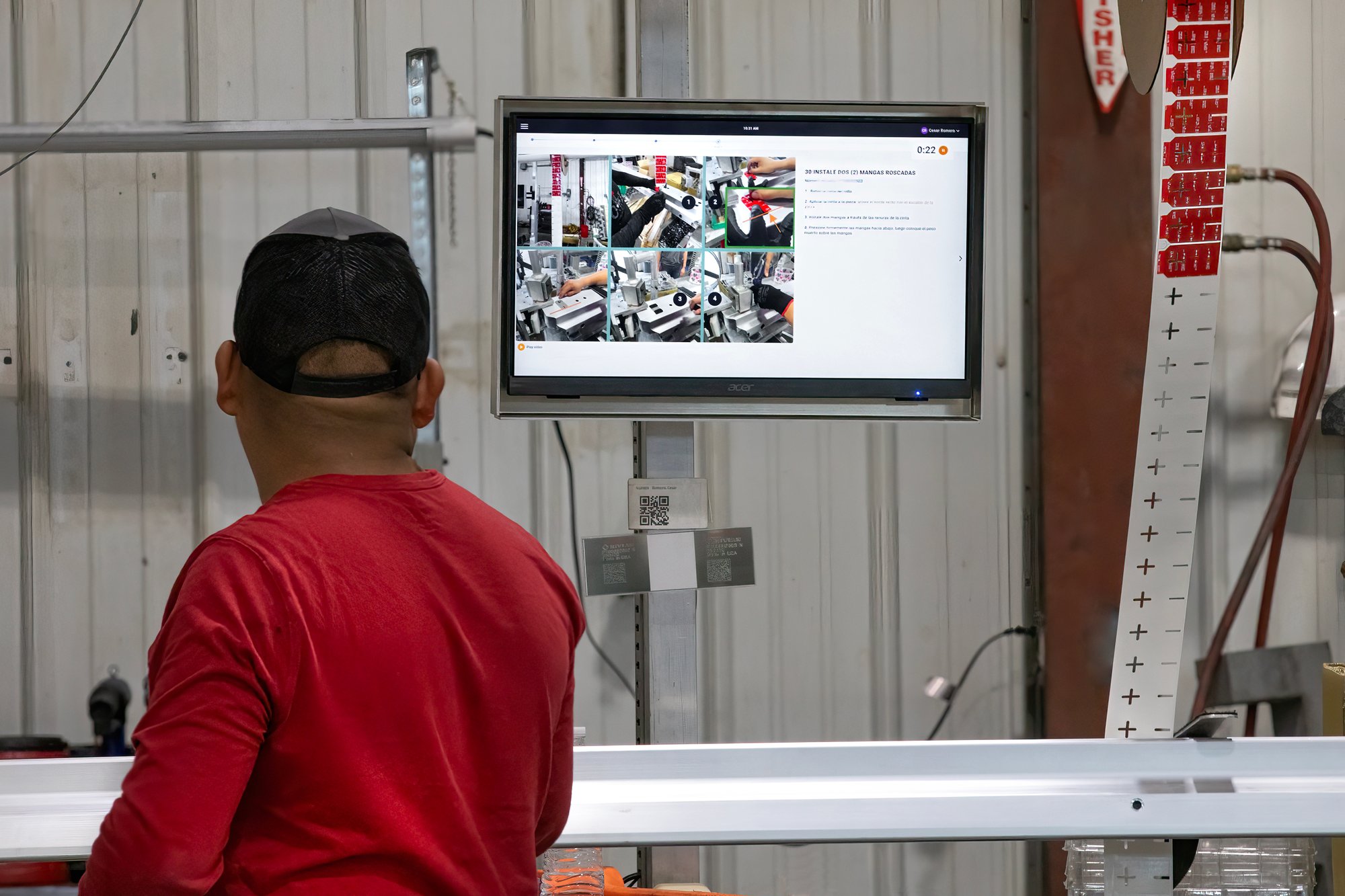

IoT Tool Integrations
Connect smart tools, devices, and machines to your MES to enable automated data capture and error-proofing.
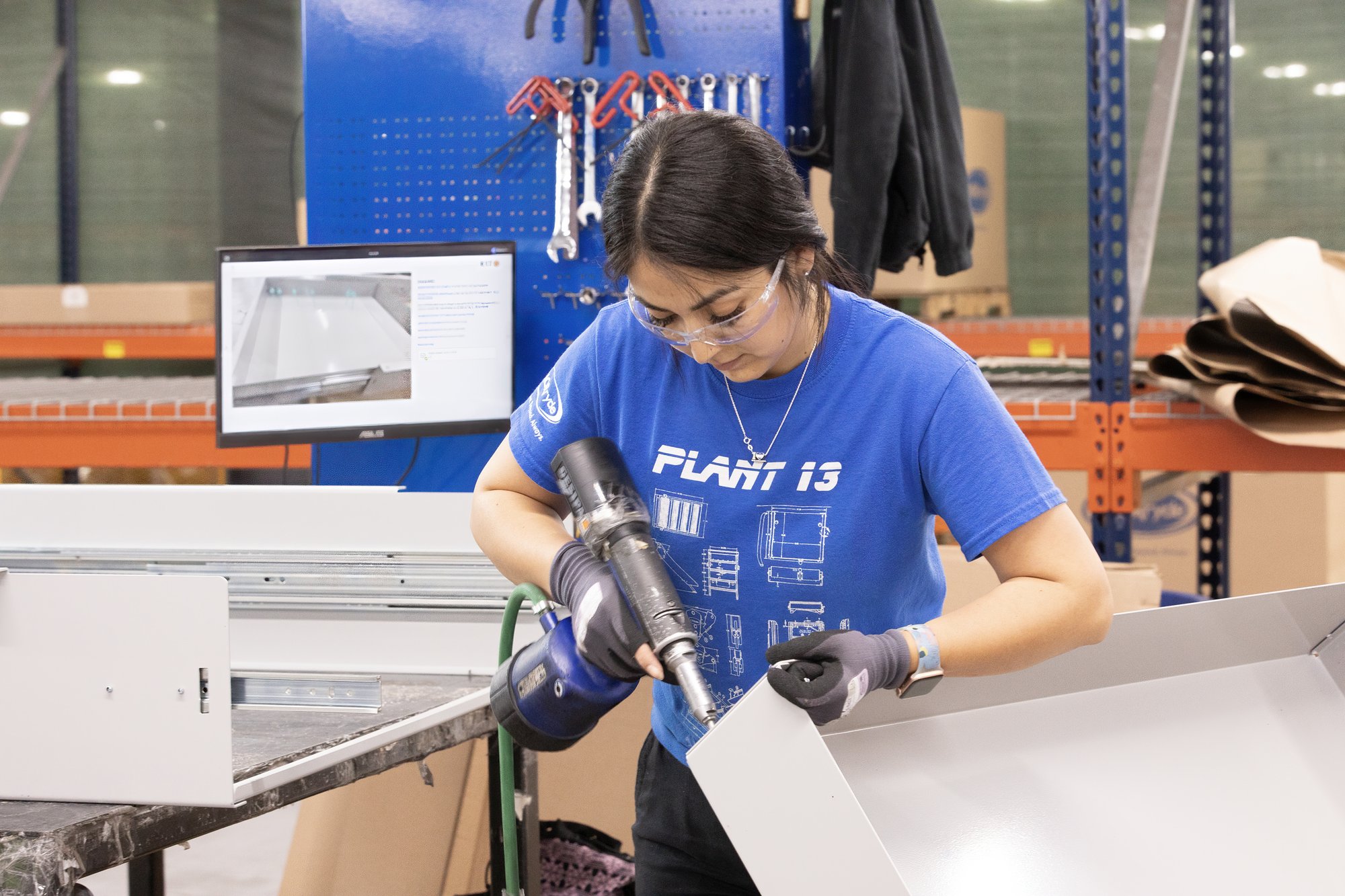

Real-Time Analytics
Gain visibility into shop floor performance and process efficiency to monitor production in real time.
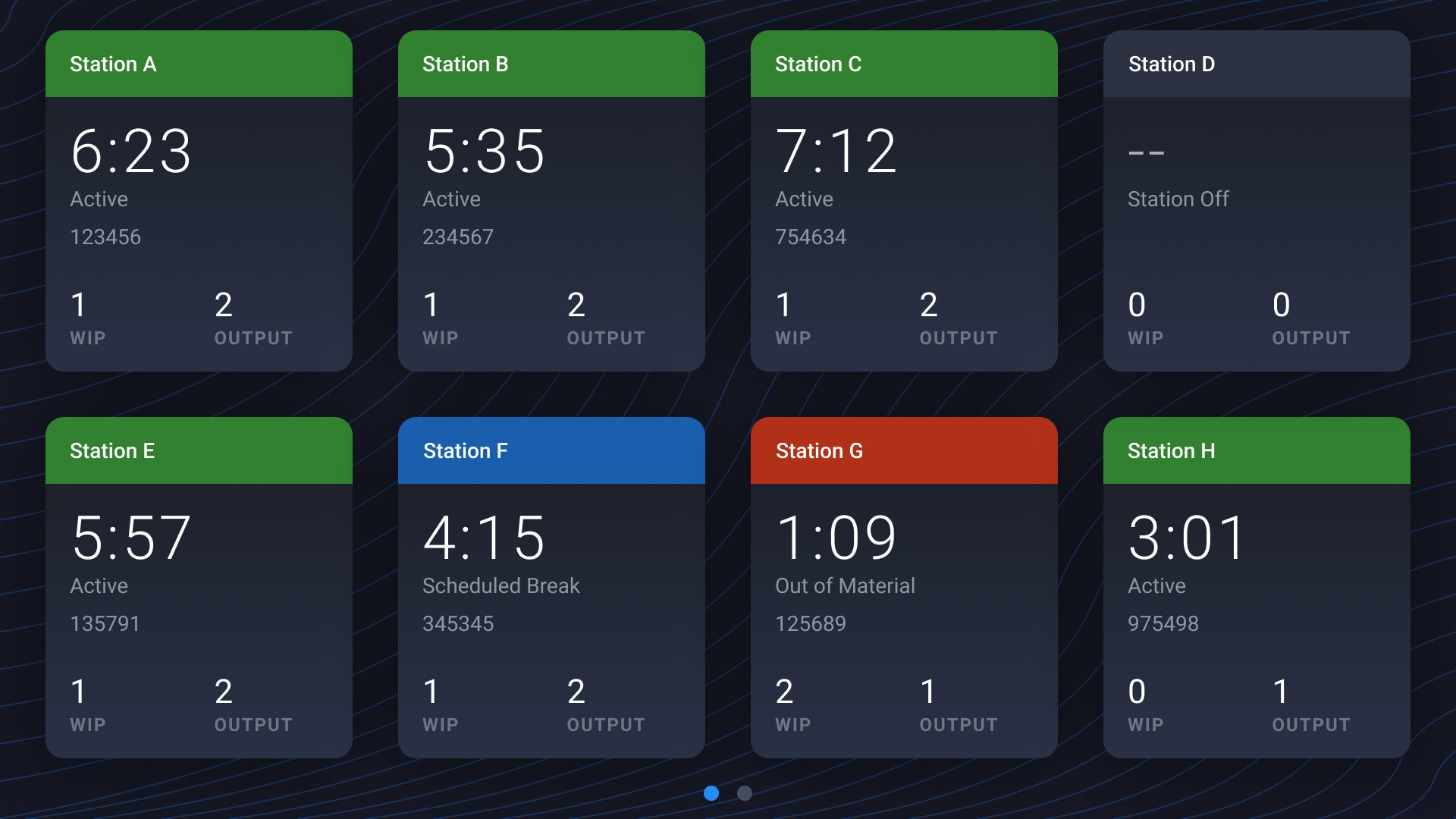
Full Backwards Traceability
Automatically capture every step of the build process. Enable real-time data collection from tools and operators, creating a complete traceability record for each unit.
ERP and System Integrations
Seamlessly sync with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, quality management software (QMS), and more to eliminate data silos and maintain consistency and transparency across the business.
These targeted capabilities can be deployed independently or together, creating a system that grows organically with your operations.
What are the Benefits of Modular MES?
Compared to traditional systems, modular MES platforms offer significant advantages:
1. Scalability
Grow from a single line to a global operation without overhauling your system.
2. Flexibility
Tailor your MES to your unique workflows, not the other way around.3. Agility
Deploy new capabilities quickly to respond to changing customer demands or process improvements.
4. Collaboration
With user-friendly tools and increased data visibility, modular MES promotes better communication between the frontline and the engineers.
The result? A more responsive, efficient manufacturing organization.
How Have Real Manufacturers Used Modular MES?
Hear real customers talk about how deploying PICO on their shop floors to digitize and error-proof processes have enabled them to improve process efficiency, product quality, and scale in their own time.
How PICO Can Help
PICO is a modular MES that delivers modern error-proofing to the shop floor. Designed with the unique challenges of assembly manufacturing in mind, our solution is made up of core features such as digital work instructions, IoT tool connectivity, real-time data capture & traceability, and seamless system integrations.
We meet manufacturers of all sizes where they’re at–whether they’re transitioning off of paper or looking for ways to leverage factory data for continuous improvement, PICO’s modular MES software is easy and fast to deploy to start solving your most pressing challenges:
- Digitizing the Shop Floor
PICO eliminates the risk of digitization by offering digital work instructions completely free of charge. Manufacturers can sign up for a cloud-based deployment to start transitioning their outdated, 2D drawings and worker guidance off of paper and out of dusty binders, onto an easy-to-use dynamic platform. - Automating Data Capture
Error-proof your assembly processes through integrated IoT tools to automatically capture and record data for full backwards traceability and real-time production analytics. Catch mistakes before they happen and reduce the risk for scrap or rework further down the line. - Continuously Improve Processes
Leverage advanced analytics and real-time operational visibility to find 1% gains every day. Connect Operations with Sales and Finance via seamless data sharing to better understand the broader impact of your production operations on the entire business.
Avoid Common MES Implementation Mistakes
Even with the right system, a poor implementation can derail progress. Here are three common pitfalls to watch out for:
1. Over-scoping the initial rollout: A common mistake is trying to solve every problem and rebuild every process in the first phase. This leads to long timelines, bloated budgets, and stalled momentum. Start small by tackling your most pressing pain points (like digitizing work instructions or adding traceability) and then expand based on operator feedback and real results. Learn how following Lean Manufacturing principles can help guide your strategy.
2. Underestimating training needs: Even intuitive tools require a culture change. Invest in onboarding and ongoing support to ensure maximum operator adoption. Get practical advice on how to get buy-in from the frontline to the front office.
3. Neglecting integration planning: A manufacturing execution system should play well with existing systems like ERP, PLM, and QMS. Integrating with your tech stack should be part of your initial planning–not an afterthought. See why you need both an MES and ERP, and why you should implement them in parallel.
Build a Flexible, Scalable Shop Floor
For assembly manufacturers looking to modernize, modular MES offers a smarter and more cost-effective path forward. It delivers the tools you need today with the flexibility to grow tomorrow. As manufacturers face rising product complexity, labor shortages, and pressure to improve efficiency, a modular approach can unlock real value where it matters most: on the shop floor.
Ready to explore modular MES for your factory? Start small, think big, and leave legacy systems in the past.
- Start digitizing your processes for free with PICO digital work instructions.
- Explore our plans & pricing to gain access to the features that will have the biggest impact on your operation
- Book a demo with our team to learn more.
FAQs About Modular vs. Monolithic MES
Can modular MES integrate with our existing ERP system?
Yes. A true modular MES is designed to integrate with your existing tech stack, including ERP, QMS, and PLM systems. This ensures consistent data across your operation without needing to rip and replace other platforms.
Do I need IT resources to manage a modular MES?
You shouldn’t; that is one of the primary advantages of a modular MES. Many modular MES solutions are built for ease of deployment and management, especially cloud-based platforms. They often require minimal IT support, especially compared to legacy systems. That said, having IT involved in integration planning is always helpful.
What’s the best way to get started with modular MES?
Start by identifying your most pressing challenge, like unclear work instructions or lack of traceability. Then, implement a single module (such as digital work instructions) in one cell or line. Collect feedback, measure improvements, and scale from there. This lean methodology approach reduces risk and accelerates ROI.
How much does a modular MES cost?
Pricing typically depends on the number of modules you choose, user licenses, and deployment scale. Because it’s modular, you only pay for what you need. Many providers (like Pico MES) offer transparent pricing and even free access to starter tools like digital work instructions.