#{ item.name }
#{ truncateText(item.metadescription) }
Quick answer: Discrete manufacturing builds countable products from individual parts—pumps, electronics, machinery, equipment. Unlike process manufacturing (mixing paint or chemicals), you can disassemble discrete products back into components.
If you've dealt with:
...you're experiencing the classic challenges of discrete manufacturing. A modular manufacturing execution system (MES) is purpose-built to solve exactly these problems by connecting your people, tools, and data on the shop floor.
What Makes Discrete Manufacturing Different?
1.You Track Individual Components (And It's Complicated)
A single product might have 50-1,000 parts. Each needs proper sourcing, tracking by revision, and verification before assembly.
The challenge: Operators grab the wrong part—especially when similar parts look nearly identical but have different specs. One wrong component can cause field failures months later.
2.You Build Multiple Product Configurations
Most discrete manufacturers build variations: different motor sizes, optional features, custom specs, and continuous engineering changes.
The challenge: Operators building 10 variants weekly need to know which procedure applies to which order. Mix-ups happen constantly with paper-based systems.
3.You Must Prove What Went into Each Product
Customers in aerospace, defense, medical, automotive, and industrial demand traceability:
The challenge: Paper travelers and spreadsheets make traceability nearly impossible. During audits, you're scrambling to piece together records, if they exist at all.
4. Products Flow Through Multiple Stations
Typical flow: Incoming inspection → Sub-assembly → Main assembly → Testing → Final inspection
The challenge: Mistakes at station 2 get discovered at station 5. By then, you've wasted labor at stations 3 and 4. Late detection = expensive rework.
What actually fixes these: Modular MES platforms with digital work instructions, connected IOT tools capturing data automatically, and manufacturing data analytics.
A modular MES addresses discrete manufacturing's unique challenges by integrating work instructions, tools, quality systems, and traceability into a single system. Here's what that looks like in practice:
Solves: Wrong parts, configuration mix-ups, engineering change lag, training difficulties
How it works: Visual, step-by-step operator guidance on monitors or touchscreens that adapts based on which product variant is being built. Photos show exactly which part to install. Updates happen instantly when engineering makes changes.

👉 Learn more about Digital Work Instructions
Solves: Wrong parts installed, out-of-spec torque, missing traceability data
How it works: Barcode scanners verify correct parts before installation. Torque wrenches won't release until you're within spec. Vision systems check component placement. Test equipment captures results automatically. Every action creates a traceability record without operator input.
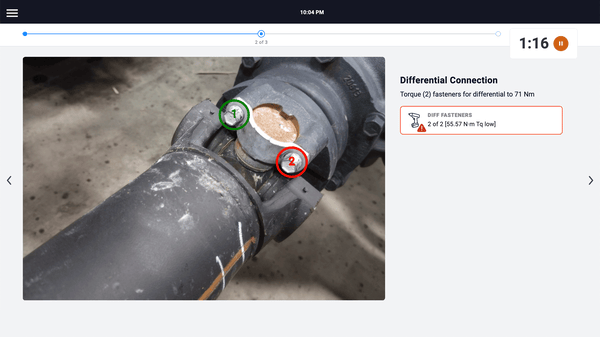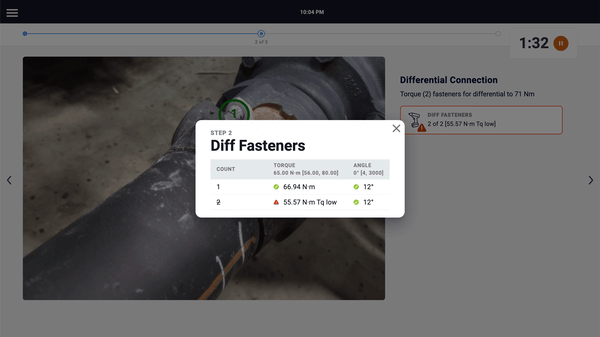
👉 Learn more about PICO's 330+ IOT device library for error-proofing
Solves: Audit preparation, recall investigations, compliance documentation
How it works: Every scan, torque reading, test result, and operator action gets recorded in real-time with timestamps and serial numbers. Pull complete build history for any product in seconds.

👉 Learn more about PICO's traceability capabilities
Solves: Late problem detection, quality inconsistency between operators and shifts
How it works: Live displays of shop floor analytics and core manufacturing KPIs like cycle time, station utlization, and more.

👉 Learn more about PICO's manufacturing data analytics features
➡️ Get started with free digital work instructions or view our Plans & Pricing for more features.
1. What is discrete manufacturing?
Discrete manufacturing is the production of distinct, countable products assembled from individual parts. Unlike process manufacturing (which mixes ingredients), discrete manufacturing creates items that can be touched, counted, and typically disassembled.
Examples include: Pumps, electronics, machinery, automotive parts, aerospace components, industrial equipment, and medical devices.
2. What is the difference between discrete and process manufacturing?
Discrete Manufacturing:
Process Manufacturing:
The distinction matters because discrete and process manufacturers face completely different operational challenges and use different types of production systems.
3. What industries use discrete manufacturing?
Discrete manufacturing is used across multiple industries:
#{ truncateText(item.metadescription) }
Bring your shop floor together — people, tools, and data all connected in one system. No rip and replace; just connections.
